JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2, Question 11
A monochromatic light is incident from air on a refracting surface of a prism of angle ![]() and refractive index
and refractive index ![]() . The other refracting surface of the prism is coated by a thin film of material of refractive index
. The other refracting surface of the prism is coated by a thin film of material of refractive index ![]() as shown in figure. The light suffers total internal reflection at the coated prism surface for an incidence angle of
as shown in figure. The light suffers total internal reflection at the coated prism surface for an incidence angle of ![]() . What is the value of
. What is the value of ![]() ?
?
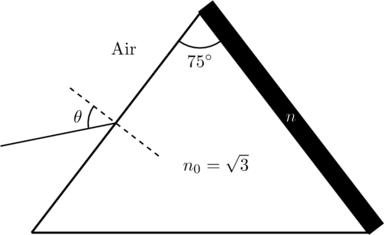
Solution
First we trace the given incident ray through the prism to find the angle at which it is incident on the opposite face (see figure below). For instance, we can extend the normals at each face (the dashed lines) to complete a quadrilateral with vertex ![]() sitting opposite the prism angle
sitting opposite the prism angle ![]() . But opposite angles of a quadrilateral are supplementary, which means
. But opposite angles of a quadrilateral are supplementary, which means ![]() .
.
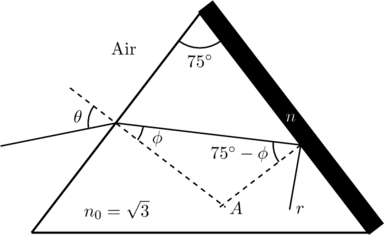
It is then apparent that the angle of incidence at the ![]() –
–![]() interface is
interface is ![]() , as indicated. Here
, as indicated. Here ![]() is the angle of refraction and it is related to
is the angle of refraction and it is related to ![]() by Snell’s Law,
by Snell’s Law,
(1) ![]()
As ![]() is increased,
is increased, ![]() shrinks, till it drops below the critical angle of the
shrinks, till it drops below the critical angle of the ![]() –
–![]() interface,
interface, ![]() . At this point total internal reflection no longer occurs. This is why the problem states that
. At this point total internal reflection no longer occurs. This is why the problem states that ![]() has an upper bound of
has an upper bound of ![]() .
.
If ![]() is exactly
is exactly ![]() the ray
the ray ![]() graces the
graces the ![]() –
–![]() interface and
interface and ![]() is the critical angle
is the critical angle ![]() , which means
, which means
(2) ![]()
The angle ![]() here can be obtained from (1) by setting
here can be obtained from (1) by setting ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
(3) ![]()
Substituting this back in (2), we find
(4) ![]()