JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 1, Question 2
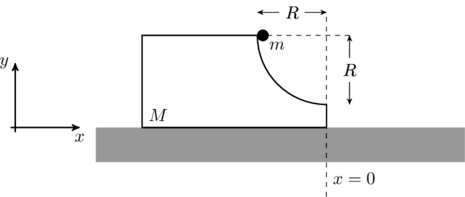
A block of mass ![]() has a circular cut with a frictionless surface as shown. The block rests on the horizontal frictionless surface of a fixed table. Initially the right edge of the block is at
has a circular cut with a frictionless surface as shown. The block rests on the horizontal frictionless surface of a fixed table. Initially the right edge of the block is at ![]() , in a co-ordinate system fixed to the table. A point mass
, in a co-ordinate system fixed to the table. A point mass ![]() is released from rest at the topmost point of the path as shown and it slides down. When the mass loses contact with the block, its position is
is released from rest at the topmost point of the path as shown and it slides down. When the mass loses contact with the block, its position is ![]() and the velocity is
and the velocity is ![]() . At that instant, which of the following options is/are correct?
. At that instant, which of the following options is/are correct?
- The position