JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 1, Question 20
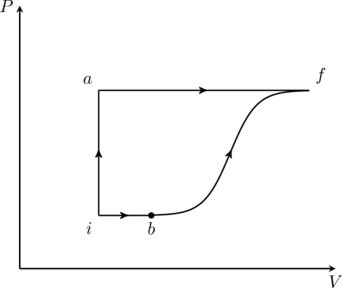
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state ![]() with internal energy
with internal energy ![]() to the final state
to the final state ![]() along two different paths
along two different paths ![]() and
and ![]() , as schematically shown in the figure. The work done by the system along the paths
, as schematically shown in the figure. The work done by the system along the paths ![]() and
and ![]() are
are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. The heat supplied to the system along the path
respectively. The heat supplied to the system along the path ![]() and
and ![]() are
are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. If the internal energy of the system in the state
respectively. If the internal energy of the system in the state ![]() is
is ![]() and
and ![]() , the ratio
, the ratio ![]() is
is
Solution
The problem gives us partial information about internal energies, heat transferred, and work done at various points in the PV diagram. We …