JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1, Question 14
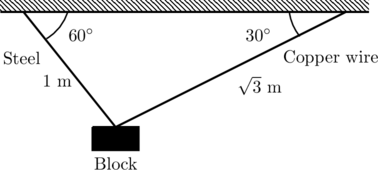
A block of weight ![]() N is suspended by copper and steel wires of same cross sectional area
N is suspended by copper and steel wires of same cross sectional area ![]() cm
cm![]() and, length
and, length ![]() m and
m and ![]() m, respectively. Their other ends are fixed on a ceiling as shown in figure. The angles subtended by copper and steel wires with ceiling are
m, respectively. Their other ends are fixed on a ceiling as shown in figure. The angles subtended by copper and steel wires with ceiling are ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively.
, respectively.
If elongation in copper wire is ![]() and elongation in steel wire is
and elongation in steel wire is ![]() , then the ratio
, then the ratio ![]() is
is
[Young’s modulus for copper and steel are ![]() N/m
N/m![]() and
and ![]() N/m
N/m![]() , respectively.]
, respectively.]
Solution
We will label the tension in the steel and copper wires by ![]() and …
and …