JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2, Question 4
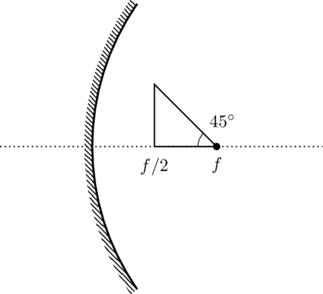
A wire is bent in the shape of a right angled triangle and is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length ![]() , as shown in the figure. Which of the figures shown in the four options qualitatively represent(s) the shape of the image of the bent wire? (These figures are not to scale.)
, as shown in the figure. Which of the figures shown in the four options qualitatively represent(s) the shape of the image of the bent wire? (These figures are not to scale.)
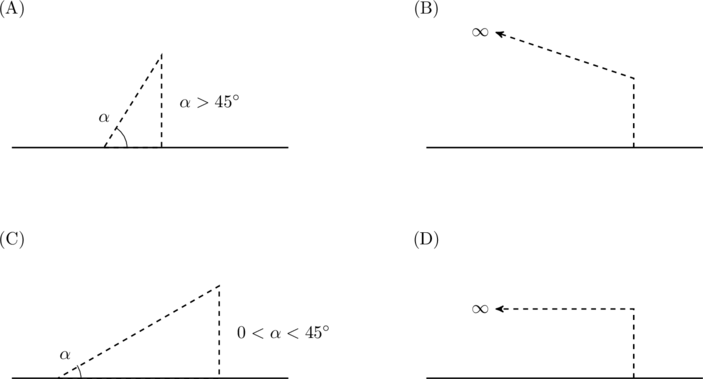
Related article: Optics without ray diagrams: Mirrors
Solution
If the object is kept between a concave mirror and its focal point the image is virtual and upright (see this note). Recall that an object at a distance …